In this article, you will get to know everything about EVM and EVM-compatible blockchains. We will explain EVM-compatible blockchains, exploring what they are, how they work, and why they are so important in the world of decentralized applications. Let’s get started.
Let’s first take a look at the basic concept of EVM.
What is EVM and how does EVM work?
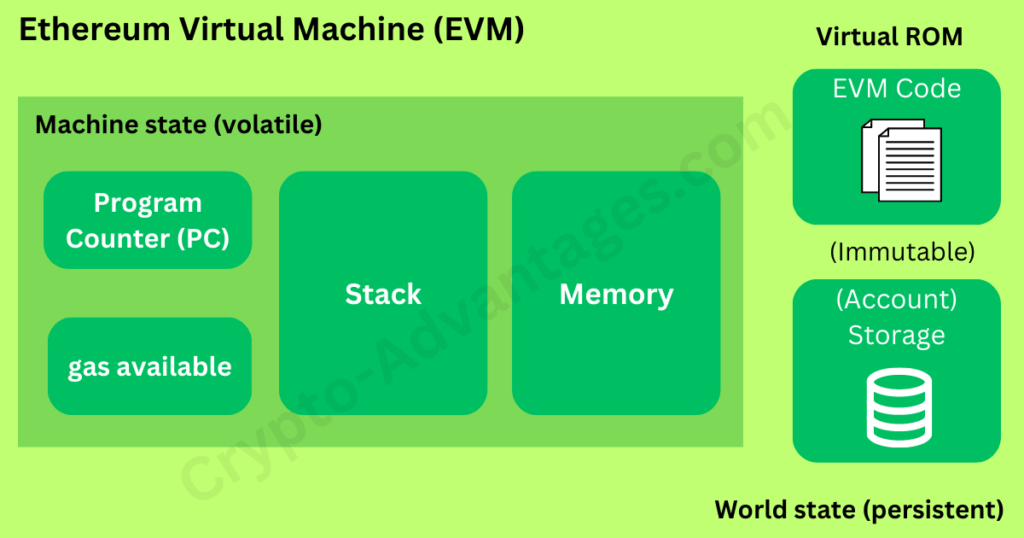
EVM stands for Ethereum Virtual Machine. The EVM is a virtual machine that runs code on the Ethereum blockchain. It offers a runtime environment for smart contracts, allowing them to be executed in a safe and decentralized manner. The status of each block in the Ethereum blockchain is determined by the EVM, a unique state machine that runs continually. This capability is effectively replicated by EVM-compatible blockchains, enabling developers to build dApps that can operate on a variety of different blockchains.
The EVM sets the particular rules of modifying state from block to block in addition to regulating what nodes can and cannot do to the distributed ledger maintained by the Ethereum blockchain.
Examining each of the several roles an Ethereum Virtual Machine plays in supporting the efficient running of the Ethereum network can help us understand what an EVM accomplishes. The EVM generates a deterministic output and follows a mathematical function for each input it gets.
Ethereum differs from other simpler blockchains like Bitcoin because of EVM’s capacity to understand and carry out smart contracts during transactions. Bitcoin blockchain is nothing but a distributed ledger. Alternately, in response to input data from a smart contract, the state transition function of the EVM enables Ethereum to update to a new valid state from block to block.
What is the use of EVM?
Without any significant downtime being observed, the EVM has been dependable in powering all apps utilizing the Ethereum network. In Ethereum, smaller executable programs are known as smart contracts. For developers, the EVM serves as the overall program that runs these contracts while giving them the ability to create these contracts in a range of programming languages, including Solidity, Python, Yul, Vyper, etc.
The Ethereum blockchain has given rise to hundreds of DApps in the non-fungible token (NFT) and decentralized finance (DeFi) spaces as a result of the freedom provided by the EVM. Each of these DApps and the underlying smart contracts are translated into bytecode, which is then disseminated among all Ethereum network nodes and fed into the EVM. When a smart contract is implemented, the EVM is in charge of interacting with every node and changing the state of the system after a consensus has been reached.
EVM: How Data is stored?
Permanent data and ephemeral data are the two different forms of data used by the Ethereum protocol. In Ethereum’s tree-like data structure, permanent data, such as a transaction, is stored and is never changed. Ephemeral data is kept track of and modified in reaction to fresh transactions, such as the amount in a wallet.
Advantages of EVM Compatible Blockchains
There are several advantages to using EVM-compatible blockchains over non-EVM blockchains. These include:
Familiarity
Developers who are already familiar with Ethereum and the EVM will find it easy to develop and deploy dApps on EVM-compatible blockchains.
Interoperability
This type of blockchains can easily communicate with each other, making it possible to create decentralized applications that span multiple blockchains.
Ecosystem
EVM-compatible blockchains benefit from the same developer ecosystem as Ethereum, including tools, libraries, and communities.
Security
By replicating the EVM functionality, EVM-compatible blockchains can offer the same level of security and decentralization as the Ethereum blockchain.
Which are EVM Compatible Blockchains?
Developers may now implement smart contracts on a wide variety of EVM-compatible blockchains, each of which has its distinct capabilities. Some of the popular EVM-compatible blockchains are listed below:
- Ethereum
- Polygon
- BNB Smart Chain
- Arbitrum
- Avalanche
- Optimism
- Cardano
- Solana
- Fantom
- Cosmos
These are only a few examples; there are many other EVM-compatible blockchains worth exploring. Each blockchain has its own set of unique features and benefits, so developers and businesses must carefully weigh the options when deciding which blockchain to utilize for their dApps.
Applications of EVM Compatible Blockchains
Blockchains that are EVM compatible have many uses and are becoming in popularity in sectors including finance, gaming, and supply chain management. The following are some of the most popular applications:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
EVM-compatible blockchains are ideal for creating DeFi applications such as decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and stablecoins.
Gaming
This type of blockchains can be used to create blockchain-based games that offer unique gameplay mechanics and tokenized assets.
Supply Chain Management
This type of blockchains can be used to create secure and transparent supply chain management systems, enabling businesses to track the movement of goods and ensure their authenticity.
As EVM-compatible blockchains continue to evolve and improve, we can expect to see an even wider range of applications and use cases emerge in the coming years.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fact that EVM-compatible blockchains may be optimized for scalability and efficiency, while simultaneously being built on top of the Ethereum network and utilizing everything it has to offer, makes them very useful.
Any application created on a blockchain that is EVM compatible is portable and interoperable with other EVM networks thanks to the EVM’s standardized environment for decentralized applications (dApps). This gives all dApps created on those blockchains access to the larger Ethereum ecosystem.
FAQs
Q1: What is EVM based Blockchains?
A: An EVM compatible blockchain is a blockchain that is capable of running smart contracts written in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) bytecode.
Q2: How many EVM blockchains are there?
A: There are currently hundreds of blockchains that are compatible with the EVM.
Q3: What does EVM compatibility mean?
A: EVM compatibility describes a blockchain’s capacity to operate the EVM and carry out Ethereum smart contracts. This implies that programmers don’t need to make major modifications to their code in order to design and deploy the same smart contracts across several EVM blockchains.
Q4: What is the largest EVM-compatible blockchain?
A: Ethereum (ETH) is the largest EVM-compatible blockchain considering TVL (Total Value Locked).
Q5: What is a non EVM blockchain?
A: Non-EVM blockchains do not adhere to the Ethereum fundamentals and do not require constant supervision by a computing engine to execute smart contracts or other protocol operations.